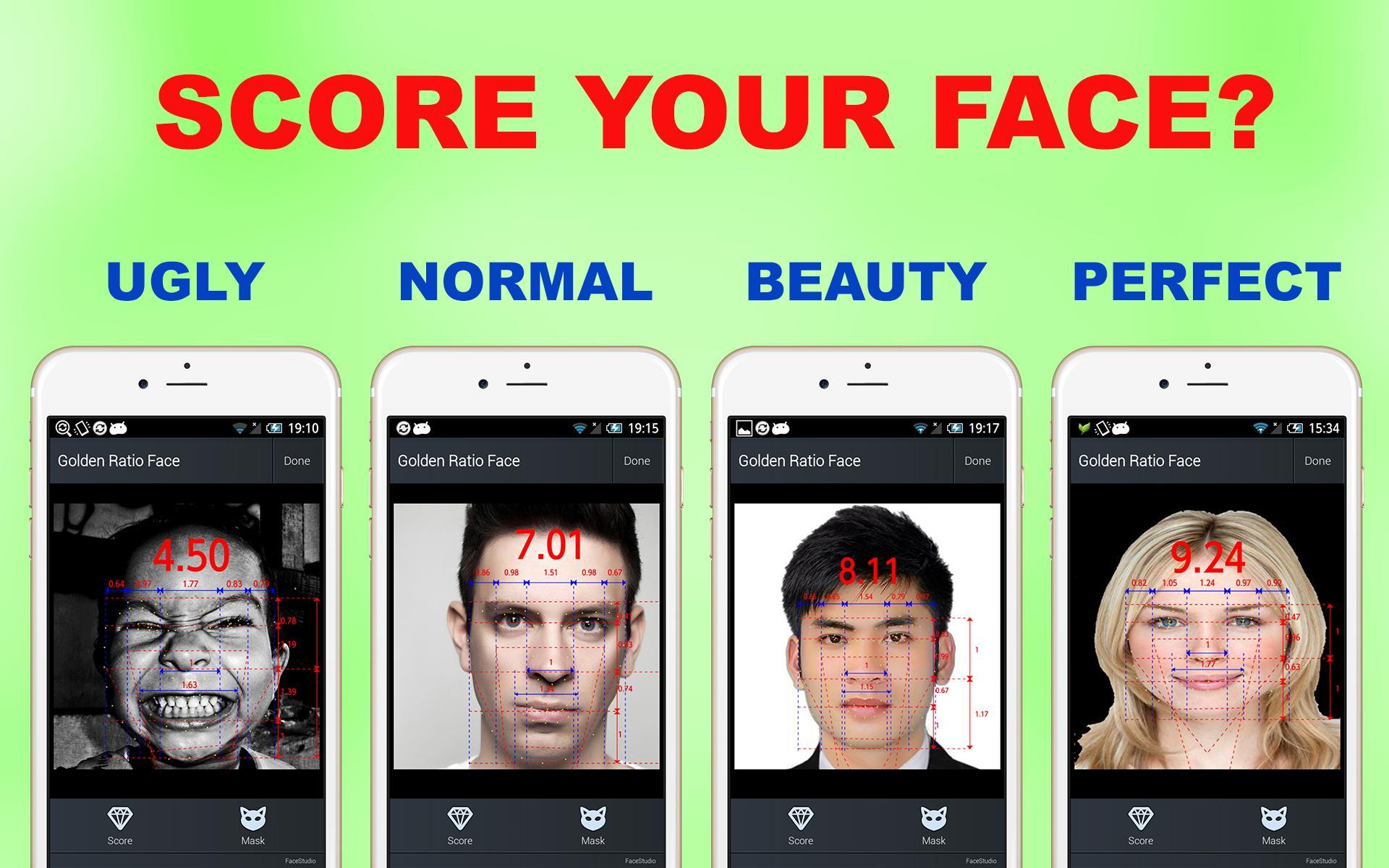
Beauty has long been a subject of fascination, and the concept of the "golden ratio face" has captivated artists, scientists, and beauty enthusiasts alike for centuries. This mathematical framework, rooted in ancient Greek philosophy, suggests that facial harmony and attractiveness can be measured by a specific ratio, known as Phi (1.618). The golden ratio has been used to analyze and define beauty in art, architecture, and now, human features.
From iconic sculptures like Michelangelo's David to the captivating allure of modern celebrities, the golden ratio face serves as a timeless benchmark for aesthetic perfection. But what exactly makes a face adhere to this golden standard? Is it purely mathematical, or does it encompass something deeper, like cultural or evolutionary influences? These questions ignite curiosity and underscore the enduring relevance of the golden ratio in both historical and contemporary contexts.
In this comprehensive guide, we'll delve into the science, history, and practical application of the golden ratio face. From understanding its origin to evaluating how modern beauty standards align with this concept, we aim to provide a full-spectrum view. Whether you're here to learn about its impact on art or to explore whether your face aligns with the golden ratio, this article is your ultimate resource.
Read also:Tags Bakery A Guide To Its Sweet Success
Table of Contents
- What is the Golden Ratio?
- History of the Golden Ratio in Art and Science
- How Does the Golden Ratio Apply to Faces?
- Facial Proportions and the Golden Ratio
- Golden Ratio Face and Modern Beauty Standards
- Is the Golden Ratio Face Universal?
- Golden Ratio in Plastic Surgery and Cosmetics
- How to Calculate Your Golden Ratio Face?
- Famous Faces and the Golden Ratio
- Can the Golden Ratio Predict Attractiveness?
- The Role of Culture in Beauty Perception
- Tools and Applications for Measuring the Golden Ratio
- Myths and Misconceptions About the Golden Ratio Face
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Conclusion
What is the Golden Ratio?
The golden ratio, denoted by the Greek letter Phi (Φ), is a mathematical ratio approximately equal to 1.618. It occurs when a line is divided into two segments in such a way that the ratio of the whole line to the longer segment is equal to the ratio of the longer segment to the shorter one. This unique proportion has fascinated mathematicians, artists, and scientists for centuries due to its occurrence in nature, art, and architecture.
In the context of human faces, the golden ratio emerges through the alignment and proportion of facial features. For example, the distance between the eyes, the width of the nose, and the length of the jawline can all be analyzed using this ratio. A face that closely aligns with the golden ratio is often perceived as more symmetrical and attractive.
The golden ratio's mathematical elegance has also been linked to natural phenomena, such as the patterns of sunflower seeds, the spirals of galaxies, and even DNA structures. Its universality makes it a fascinating topic for those interested in understanding the interplay between science and aesthetics.
History of the Golden Ratio in Art and Science
The golden ratio has its roots in ancient Greece, where philosophers like Pythagoras and Euclid explored its properties. It was later popularized during the Renaissance by artists like Leonardo da Vinci, who used it to create visually harmonious compositions. Da Vinci's "Vitruvian Man" is a prime example of how the golden ratio has been applied to the human form.
In science, the golden ratio has influenced fields ranging from biology to astronomy. For instance, the Fibonacci sequence, closely related to the golden ratio, appears in the arrangement of leaves, the branching of trees, and the structure of seashells. This cross-disciplinary relevance underscores its significance as a universal principle.
Over time, the golden ratio has transcended its mathematical origins to become a cultural symbol of beauty, balance, and perfection. Its application to human faces is a relatively modern phenomenon, driven by advancements in technology and a growing interest in quantifying beauty.
Read also:Mastering Dunstan Baby Language A Parents Guide To Understanding Infant Communication
How Does the Golden Ratio Apply to Faces?
The application of the golden ratio to human faces involves measuring specific proportions and comparing them to the ideal 1.618 ratio. Key areas of focus include:
- The ratio of the length of the face to its width.
- The proportion of the forehead to the rest of the face.
- The symmetry of facial features, such as the eyes, nose, and lips.
While no face perfectly adheres to the golden ratio, those that come close are often perceived as more attractive. This perception is thought to be rooted in evolutionary psychology, as symmetrical and proportionate features may signal good health and genetic fitness.
Advancements in facial mapping technology have made it easier to analyze how closely a face aligns with the golden ratio. These tools are widely used in fields like plastic surgery, cosmetics, and even dating apps to assess and enhance facial attractiveness.
Facial Proportions and the Golden Ratio
What are the key facial proportions measured?
Facial proportions are evaluated by dividing the face into three horizontal sections:
- From the hairline to the eyebrows.
- From the eyebrows to the base of the nose.
- From the base of the nose to the chin.
Each section should ideally align with the golden ratio for a balanced appearance. Additionally, the width of the nose, the distance between the eyes, and the shape of the jawline are also analyzed.
Why is symmetry important in facial aesthetics?
Symmetry is often associated with health, youth, and genetic fitness, making it a key factor in perceived beauty. While perfect symmetry is rare, faces that are more symmetrical are generally considered more attractive. The golden ratio serves as a guideline for achieving this symmetry in facial proportions.
Golden Ratio Face and Modern Beauty Standards
In today's image-conscious society, the golden ratio face has become a benchmark for beauty. Celebrities like Beyoncé, Angelina Jolie, and Robert Pattinson are often cited as examples of individuals whose facial features closely align with the golden ratio. This has fueled public interest in understanding and achieving this ideal.
However, it's important to note that beauty is subjective and influenced by cultural, social, and individual factors. While the golden ratio provides a mathematical framework, it is not the sole determinant of attractiveness.
Is the Golden Ratio Face Universal?
The universality of the golden ratio face is a subject of debate. While its principles are rooted in mathematics and science, cultural differences play a significant role in defining beauty standards. What is considered attractive in one culture may not hold the same appeal in another.
For example, in some cultures, fuller lips and darker skin tones are celebrated, while others may prioritize lighter skin and angular features. These variations highlight the complexity of beauty and the limitations of applying a universal standard like the golden ratio to diverse populations.
Golden Ratio in Plastic Surgery and Cosmetics
The golden ratio has found practical applications in the fields of plastic surgery and cosmetics. Surgeons and makeup artists often use this principle to enhance facial symmetry and proportions. Techniques like rhinoplasty, lip augmentation, and contouring are designed to bring features closer to the golden ratio.
While these procedures can enhance facial harmony, they should be approached with caution. Achieving the golden ratio is not always feasible, and the pursuit of perfection can sometimes lead to unrealistic expectations.
How to Calculate Your Golden Ratio Face?
Calculating your golden ratio face involves measuring key facial proportions and comparing them to the ideal 1.618 ratio. Several online tools and apps can assist with this process, allowing you to upload a photo and receive an analysis of your facial symmetry and proportions.
While these tools provide a fun way to explore the concept, they should not be taken too seriously. Beauty is multifaceted and cannot be reduced to a single mathematical equation.
Famous Faces and the Golden Ratio
Many celebrities are often cited as examples of golden ratio faces. Studies have analyzed the facial features of stars like Beyoncé, Taylor Swift, and George Clooney, revealing how closely they align with the 1.618 proportion. These findings have further popularized the golden ratio as a standard for beauty.
Can the Golden Ratio Predict Attractiveness?
While the golden ratio provides a useful framework for analyzing facial proportions, it is not a definitive predictor of attractiveness. Beauty is subjective and influenced by a range of factors, including personality, confidence, and cultural norms.
That said, the golden ratio can offer valuable insights into the mathematical principles underlying human aesthetics, making it a fascinating topic for further exploration.
The Role of Culture in Beauty Perception
Cultural factors play a significant role in shaping beauty standards. What is considered attractive in one part of the world may differ greatly from another. This cultural diversity underscores the limitations of applying a universal standard like the golden ratio to facial aesthetics.
Tools and Applications for Measuring the Golden Ratio
Several tools and applications are available for measuring the golden ratio in human faces. These include software programs, mobile apps, and even physical templates used by artists and surgeons. While these tools can provide valuable insights, they should be used as guidelines rather than absolute standards.
Myths and Misconceptions About the Golden Ratio Face
Despite its scientific basis, the golden ratio face is often surrounded by myths and misconceptions. Some people mistakenly believe that it is the sole determinant of beauty, while others view it as an unattainable ideal. Understanding the limitations and context of this concept is essential for a balanced perspective.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is the golden ratio face?
The golden ratio face refers to a face whose proportions align closely with the mathematical ratio of 1.618, known as Phi. This ratio is believed to contribute to perceived beauty and symmetry.
2. How do I know if my face matches the golden ratio?
You can use online tools, apps, or consult a professional to analyze your facial proportions and compare them to the golden ratio. However, beauty is subjective and cannot be fully quantified.
3. Is the golden ratio scientifically proven?
While the golden ratio has a strong mathematical basis, its application to beauty is not universally accepted. It is one of many factors that contribute to perceived attractiveness.
4. Can the golden ratio be achieved through plastic surgery?
Plastic surgery can enhance facial symmetry and proportions, bringing features closer to the golden ratio. However, it is not always possible or necessary to achieve this ideal.
5. Are there cultural differences in the perception of the golden ratio face?
Yes, cultural factors play a significant role in beauty standards. The golden ratio is just one of many frameworks used to analyze facial aesthetics.
6. Why is the golden ratio significant in art and science?
The golden ratio is significant because it appears in various natural and man-made phenomena, from the spirals of galaxies to the proportions of famous artworks. Its universality makes it a fascinating subject of study.
Conclusion
The golden ratio face represents a captivating intersection of mathematics, art, and beauty. While it offers valuable insights into the principles of facial harmony, it is not the sole determinant of attractiveness. Beauty is a multifaceted concept, influenced by a blend of cultural, personal, and evolutionary factors.
Whether you’re exploring the golden ratio for personal curiosity or professional application, it’s essential to approach it as a guideline rather than an absolute standard. After all, the true essence of beauty lies in diversity and individuality, which cannot be fully captured by a single mathematical formula.
For those intrigued by the concept, the golden ratio serves as a reminder of the intricate connections between science and aesthetics, encouraging us to appreciate both the measurable and the immeasurable aspects of beauty.