In the vast realm of human anatomy and cognition, the term "big brain" often sparks curiosity and intrigue. It points to not just the physical size of the brain but also its remarkable capabilities. The human brain is an enigmatic organ that orchestrates all bodily functions, thoughts, and emotions. Understanding the dynamics behind what comprises a "big brain" can provide insights into human intelligence, creativity, and potential. This article endeavors to delve deep into the elements that constitute a big brain, exploring its biological, psychological, and theoretical dimensions.
The concept of a big brain isn't limited to its size alone; it involves a complex interplay of neurons, synapses, and chemical processes that drive intelligence and cognitive functions. It's the intricate network of connectivity that allows humans to solve problems, create art, and communicate ideas. The brain's capacity for neuroplasticity, or the ability to reorganize itself by forming new neural connections, plays a pivotal role in learning and adaptation. As we embark on this exploration, we'll uncover how a big brain influences personality, behavior, and even societal evolution.
In a world increasingly driven by technology and information, understanding the big brain becomes ever more relevant. This knowledge can not only enhance educational methodologies and mental health strategies but also offer new perspectives on artificial intelligence and robotics. By examining the historical, present, and future aspects of the big brain, this article aims to provide a comprehensive understanding that is both informative and thought-provoking. So, let's embark on this intellectual journey to unravel the mysteries of the big brain.
Read also:Everything You Need To Know About Sedona Slate Features Benefits And Applications
Table of Contents
- What is the Biological Basis of a Big Brain?
- The Evolutionary Significance of a Big Brain
- How Does Neuroplasticity Influence the Big Brain?
- Cognitive Functions of a Big Brain
- The Relationship Between Big Brain and Intelligence
- Creativity and the Big Brain
- How Does Emotional Intelligence Relate to a Big Brain?
- Big Brain and Its Impact on Society
- The Role of Big Brain in Mental Health
- Big Brain in the Context of Artificial Intelligence
- What are the Educational Implications of a Big Brain?
- Future Prospects for Big Brain Research
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Conclusion
What is the Biological Basis of a Big Brain?
The biological foundation of a big brain encompasses its physical structure, including the cerebral cortex, which is pivotal for advanced cognitive processes. The human brain is composed of approximately 86 billion neurons, each forming intricate networks that facilitate communication and information processing. The cerebral cortex, known as the "gray matter," is responsible for higher-order functions such as perception, reasoning, and language.
Moreover, the brain's size relative to body size, known as the encephalization quotient (EQ), is a significant factor in understanding the big brain concept. Humans have a high EQ, indicating a disproportionately large brain compared to body size, which correlates with complex cognitive abilities. Factors influencing brain size include genetic inheritance, environmental stimuli, and nutritional influences during developmental stages.
Recent advancements in neuroimaging have provided deeper insights into the brain's structure and function. Techniques such as magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and positron emission tomography (PET) scans allow scientists to observe brain activity and identify areas associated with specific functions. These technologies have been instrumental in linking brain structure to cognitive capabilities, further illuminating the biological underpinnings of a big brain.
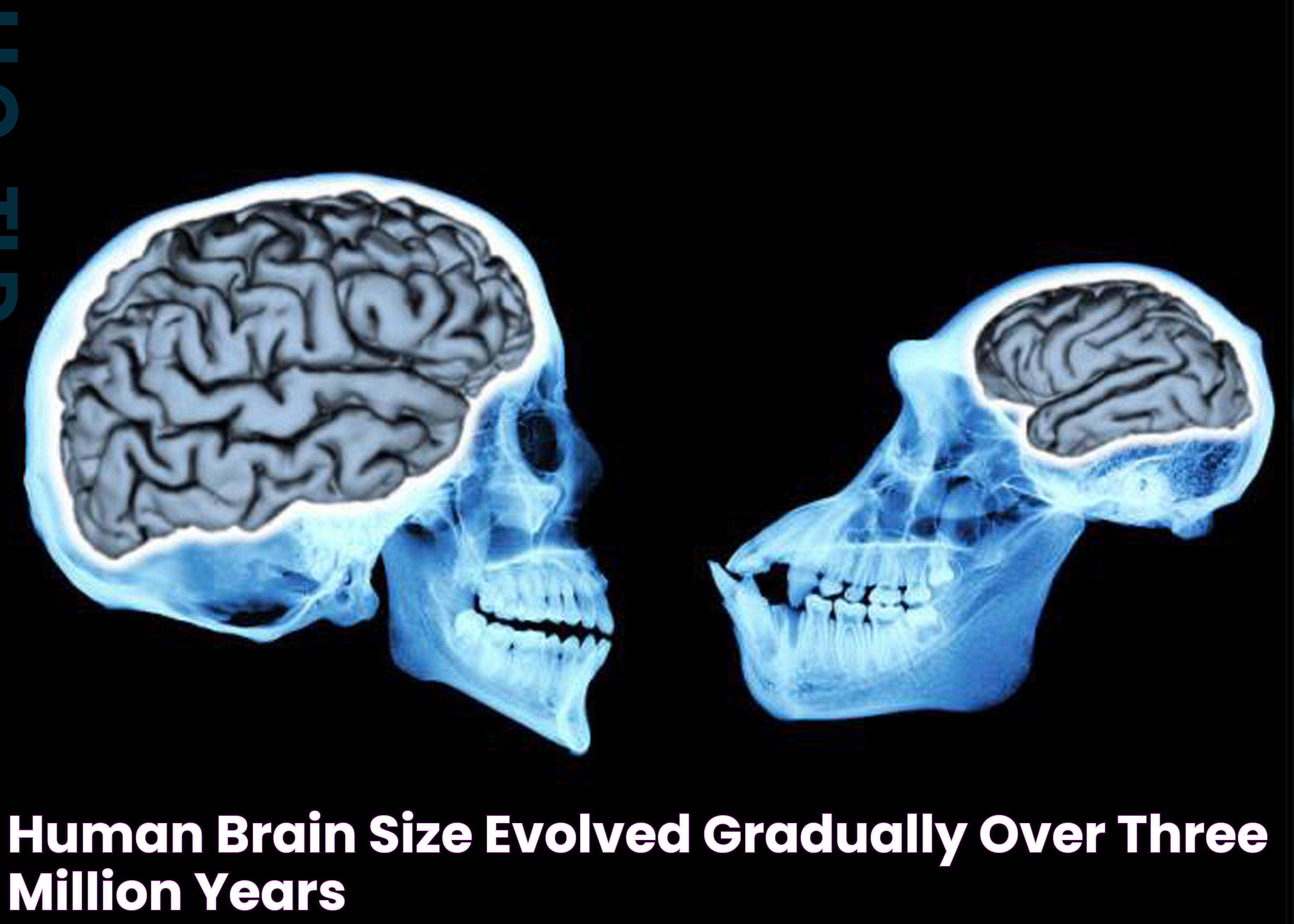
The Evolutionary Significance of a Big Brain
The evolution of the human brain is a testament to the species' adaptability and survival prowess. The enlargement of the brain, particularly the frontal lobes, has been associated with the development of complex social behaviors, problem-solving skills, and cultural advancements. The shift from a primarily instinct-driven existence to one characterized by foresight and planning underscores the evolutionary importance of a big brain.
Throughout evolutionary history, periods of significant brain growth coincided with major environmental changes and the emergence of new survival challenges. The development of tools, language, and social structures required enhanced cognitive functions, which were facilitated by a larger brain. This evolutionary trajectory highlights the role of natural selection in favoring individuals with superior cognitive abilities, ultimately contributing to the species' dominance.
Furthermore, the evolutionary significance of a big brain extends to its impact on human behavior and societal development. It has enabled humans to create complex social networks, engage in cooperative activities, and establish civilizations. As such, the big brain is not merely a product of evolution but a driving force behind humanity's progress and innovation.
Read also:Ultimate Guide To Greek Islands Chicago A Mediterranean Escape In The Windy City
How Does Neuroplasticity Influence the Big Brain?
Neuroplasticity, the brain's ability to reorganize itself by forming new neural connections, is a cornerstone of the big brain's adaptability. It allows the brain to recover from injuries, adapt to new experiences, and learn new information throughout a person's life. This remarkable capability underscores the dynamic nature of the brain and its potential for growth and change.
Neuroplasticity is influenced by various factors, including age, environment, and experiences. While the brain is most malleable during childhood, it retains a degree of plasticity throughout adulthood. Engaging in activities that challenge the brain, such as learning new skills or solving puzzles, can enhance neuroplasticity and promote cognitive health.
Research in neuroplasticity has profound implications for education, therapy, and rehabilitation. It suggests that cognitive abilities can be improved through targeted interventions and training programs. By harnessing the principles of neuroplasticity, individuals can optimize their brain function and maintain cognitive vitality well into old age.
Cognitive Functions of a Big Brain
The cognitive functions of a big brain encompass a wide range of mental processes, including attention, memory, language, and executive functions. These functions are essential for navigating the complexities of daily life and achieving personal and professional goals. The big brain's capacity for processing and integrating information is unparalleled, enabling humans to perform tasks that require abstract thinking and problem-solving.
Attention, the ability to focus on specific stimuli while ignoring others, is a critical cognitive function facilitated by the brain's attentional networks. Memory, another vital function, involves encoding, storing, and retrieving information. The hippocampus, a key structure within the brain, plays a central role in memory formation and recall.
Language, a hallmark of human cognition, is mediated by specialized areas in the brain, such as Broca's and Wernicke's areas. These regions work in concert to enable speech production and comprehension. Executive functions, which include planning, decision-making, and impulse control, are governed by the prefrontal cortex. Together, these cognitive functions illustrate the remarkable capabilities of a big brain.
The Relationship Between Big Brain and Intelligence
The relationship between a big brain and intelligence is a subject of ongoing research and debate. Intelligence, often measured by IQ tests, encompasses a range of cognitive abilities, including logical reasoning, problem-solving, and adaptability. While brain size does not directly equate to intelligence, there is a correlation between the two, particularly when considering neural connectivity and efficiency.
Studies suggest that individuals with larger brains tend to perform better on intelligence tests, although this is not a definitive rule. The organization and density of neural networks, rather than sheer size, play a crucial role in determining cognitive abilities. Efficient neural processing allows for faster and more accurate information retrieval, contributing to higher intelligence.
Moreover, intelligence is influenced by a combination of genetic, environmental, and cultural factors. While the big brain provides a biological foundation for intelligence, it is shaped and refined through experiences and learning. This multifaceted relationship highlights the complexity of intelligence and the role of the big brain in its development.
Creativity and the Big Brain
Creativity, the ability to generate novel and valuable ideas, is closely linked to the big brain's cognitive capabilities. It involves divergent thinking, which requires flexibility, originality, and the ability to see connections between seemingly unrelated concepts. The big brain's capacity for imagination and innovation is a testament to its creative potential.
Creativity is facilitated by the brain's default mode network (DMN), a collection of interconnected brain regions that activate during rest and introspection. The DMN plays a crucial role in idea generation and spontaneous thought, which are key components of the creative process. Additionally, the prefrontal cortex, responsible for executive functions, aids in the evaluation and refinement of creative ideas.
Fostering creativity involves cultivating an environment that encourages exploration and experimentation. Exposure to diverse experiences, cultures, and perspectives can stimulate creative thinking and enhance the brain's ability to generate innovative solutions. The big brain's potential for creativity underscores its role in driving progress and cultural evolution.
How Does Emotional Intelligence Relate to a Big Brain?
Emotional intelligence (EI), the ability to perceive, understand, and manage emotions, is an integral aspect of a big brain's functionality. It encompasses skills such as empathy, emotional regulation, and interpersonal communication, which are essential for building and maintaining relationships.
The big brain's limbic system, particularly the amygdala and prefrontal cortex, plays a central role in processing emotions and facilitating emotional intelligence. The amygdala is responsible for detecting and responding to emotional stimuli, while the prefrontal cortex regulates emotional responses and decision-making.
Developing emotional intelligence involves enhancing self-awareness and social skills through practice and reflection. It contributes to personal well-being, effective communication, and conflict resolution. The big brain's capacity for emotional intelligence underscores its significance in fostering positive social interactions and emotional resilience.
Big Brain and Its Impact on Society
The influence of a big brain extends beyond individual cognition to shape societal structures and cultural norms. It has enabled humans to develop complex societies characterized by cooperation, innovation, and cultural diversity. The big brain's role in communication, problem-solving, and creativity has facilitated the development of language, technology, and art.
Throughout history, societies with advanced cognitive capabilities have been able to adapt to environmental challenges, develop new technologies, and establish trade networks. The big brain's impact on societal evolution is evident in the rise of civilizations and the progression of human culture.
Moreover, the big brain's influence on society is reflected in contemporary issues such as education, mental health, and technology. Understanding the big brain's capabilities can inform policies and practices that promote cognitive development and societal well-being. As such, the big brain is a driving force behind human progress and innovation.
The Role of Big Brain in Mental Health
Mental health, a critical aspect of overall well-being, is intricately linked to the functioning of the big brain. Conditions such as depression, anxiety, and schizophrenia are associated with imbalances in brain chemistry and disruptions in neural connectivity. Understanding the big brain's role in mental health is essential for developing effective interventions and treatments.
The big brain's neurotransmitter systems, including serotonin, dopamine, and norepinephrine, play a crucial role in regulating mood and emotional responses. Imbalances in these systems can lead to mental health disorders, highlighting the importance of maintaining brain health for emotional well-being.
Advancements in neuroscience have led to the development of therapies and medications that target specific brain regions and neurotransmitter systems. These interventions aim to restore balance and improve mental health outcomes. The big brain's role in mental health underscores the need for continued research and innovation in the field of psychiatry and psychology.
Big Brain in the Context of Artificial Intelligence
The concept of a big brain has profound implications for the development of artificial intelligence (AI) and robotics. By understanding the brain's structure and functions, scientists and engineers can create intelligent systems that mimic human cognition and behavior. The big brain serves as a model for designing AI algorithms that exhibit learning, reasoning, and problem-solving capabilities.
AI technologies, such as neural networks and machine learning, draw inspiration from the brain's neural architecture and plasticity. These technologies have the potential to revolutionize industries by automating tasks, enhancing decision-making, and creating new opportunities for innovation.
However, the development of AI also raises ethical and societal questions about the implications of creating machines with cognitive abilities akin to the big brain. Balancing technological advancement with ethical considerations is crucial for ensuring the responsible and beneficial integration of AI into society.
What are the Educational Implications of a Big Brain?
The big brain's capabilities have significant implications for education and learning. Understanding how the brain processes information and adapts to new experiences can inform teaching strategies and educational practices. The big brain's capacity for learning and memory is a testament to its potential for academic achievement and personal growth.
Educational approaches that leverage the principles of neuroplasticity and cognitive development can enhance learning outcomes and foster a love of learning. Personalized and experiential learning, which cater to individual learning styles and preferences, can optimize brain function and promote cognitive engagement.
Furthermore, the big brain's role in education extends to lifelong learning and skill development. In an ever-changing world, cultivating a mindset of continuous learning and adaptability is essential for personal and professional success. The big brain's educational implications underscore the importance of fostering a culture that values knowledge and intellectual growth.
Future Prospects for Big Brain Research
The future of big brain research is promising, with ongoing advancements in neuroscience, technology, and cognitive science. Emerging research areas, such as brain-computer interfaces (BCIs) and neuroenhancement, offer exciting possibilities for enhancing brain function and expanding human capabilities.
BCIs, which enable direct communication between the brain and external devices, have the potential to revolutionize fields such as medicine, rehabilitation, and communication. These technologies can restore lost functions, enhance cognitive abilities, and even facilitate human-computer interactions.
Neuroenhancement, the use of interventions to improve cognitive function, is another area of interest. This includes the development of pharmaceuticals, brain stimulation techniques, and cognitive training programs aimed at optimizing brain performance.
As research continues to uncover the mysteries of the big brain, it will undoubtedly lead to new insights and applications that enhance human potential and improve quality of life. The future prospects for big brain research are vast and hold the promise of a deeper understanding of the human mind.
Frequently Asked Questions
- What is the difference between brain size and cognitive ability?
Brain size refers to the physical dimensions of the brain, while cognitive ability encompasses mental processes such as thinking, learning, and problem-solving. While there is some correlation between brain size and cognitive ability, the organization and efficiency of neural networks play a more significant role in determining cognitive capabilities.
- Can neuroplasticity occur in adults?
Yes, neuroplasticity can occur in adults, although the brain is most malleable during childhood. Engaging in activities that challenge the brain, such as learning new skills or solving puzzles, can enhance neuroplasticity and promote cognitive health in adulthood.
- How can I enhance my brain's creativity?
Enhancing creativity involves cultivating an environment that encourages exploration and experimentation. Exposure to diverse experiences, cultures, and perspectives can stimulate creative thinking and enhance the brain's ability to generate innovative solutions.
- What role does the big brain play in emotional intelligence?
The big brain's limbic system, particularly the amygdala and prefrontal cortex, plays a central role in processing emotions and facilitating emotional intelligence. These regions are responsible for detecting, responding to, and regulating emotional stimuli.
- What are the implications of big brain research for AI development?
Big brain research informs the development of AI technologies by providing insights into human cognition and behavior. AI systems, such as neural networks and machine learning, draw inspiration from the brain's neural architecture and plasticity, enabling them to exhibit learning, reasoning, and problem-solving capabilities.
- How does the big brain influence mental health?
The big brain's neurotransmitter systems play a crucial role in regulating mood and emotional responses. Imbalances in these systems can lead to mental health disorders, highlighting the importance of maintaining brain health for emotional well-being. Understanding the big brain's role in mental health is essential for developing effective interventions and treatments.
Conclusion
The concept of a big brain encompasses a multitude of facets, from its biological foundations to its cognitive and societal implications. It highlights the brain's incredible capacity for intelligence, creativity, and emotional understanding. As we continue to explore the mysteries of the big brain, we gain insights that have the potential to transform education, mental health, and technology. With a blend of scientific inquiry and practical application, the big brain remains a testament to human potential and the limitless possibilities of the mind.